From your brain to your toes, cigarette smoking health effects can wreak havoc on every inch of your body. In this eye-opening blog post, we’ll take you on a journey from A to Z, exploring just how damaging cigarettes can be to your health. Prepare yourself for some shocking facts and real-life stories that will make you think twice before lighting up again. It’s time to dive deep into the detrimental effects of smoking on every part of your body – are you ready?
Introduction to cigarette smoking health effects and its impact on health
Smoking has been a prevalent activity for centuries, tracing back to ancient rituals and ceremonies. However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that the harmful effects of smoking on our health were fully understood. And despite numerous efforts to educate about the risks and discourage tobacco use, cigarettes remain one of the leading preventable causes of death worldwide.
The National Cancer Institute defines smoking as ‘the inhalation of smoke from burning tobacco enclosed within cigarettes, pipes, or cigars.’ This smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, with at least 250 known to be poisonous and more than 70 causing cancer. These toxic substances include tar, carbon monoxide, nicotine, formaldehyde, ammonia, benzene and many more. When inhaled into our lungs regularly through smoking, they can cause severe damage to our body’s systems.
Let’s take a closer look at how cigarette smoking health affects every part of your body:
1) Respiratory System:
Our respiratory system includes organs such as lungs and airways that are necessary for breathing. Smoking damages these organs by depositing harmful chemicals directly onto their tissues. The smoke irritates airways causing inflammation and swelling which leads to respiratory problems like chronic bronchitis or emphysema. It also increases mucus production resulting in coughs and shortness of breath.
2) Cardiovascular System:
The heart beats continuously to pump blood throughout our body providing oxygen and nutrients essential for life. However, when we inhale cigarette smoke toxins enter our bloodstream causing plaque build-up in arteries affecting their ability to function correctly. This results in an increased risk of heart diseases like coronary artery disease (CAD), stroke or even heart attack.
3) Digestive System:
Cigarette smoking health affects your digestive system by increasing the chances of developing gastrointestinal disorders like ulcers or Crohn’s disease due to reduced blood flow caused by narrowed blood vessels. It also contributes significantly to the development of colorectal cancer due to harmful substances in tobacco.
4) Musculoskeletal System:
Nicotine in cigarettes constricts blood vessels, limiting oxygen supply to muscles, and contributes towards increasing muscle tension and pain. This reduces physical endurance making simple tasks like climbing stairs more difficult. Cigarette smoking health effects also weakens bones leading to osteoporosis, which makes one more prone to fractures.
Cigarette smoking health affects every part of our body and leaves no system untouched. It is not surprising that it is one of the leading causes of preventable diseases and death globally. Therefore, quitting smoking is essential for your overall health and well-being. In the next section, we will further discuss the impact of cigarette smoking health effects on different parts of your body in detail.
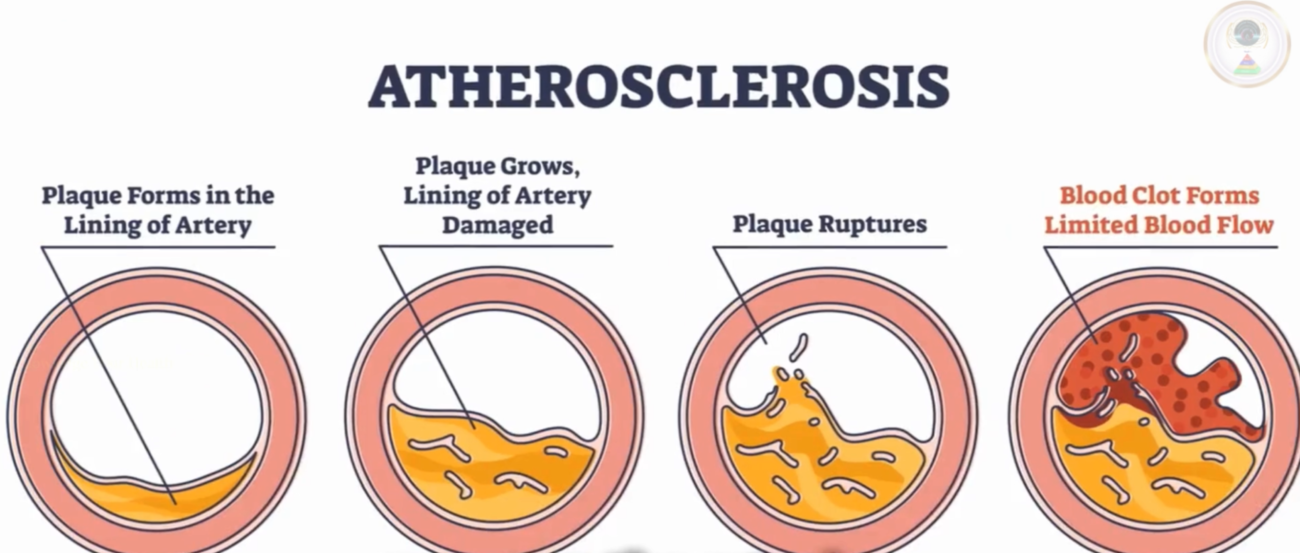
Arteries
When it comes to cigarette smoking, most people are aware of the damage it can do to their lungs. However, what is often overlooked is the harm it causes to our blood vessels. The arteries, in particular, are greatly affected by cigarette smoking.
Firstly, let’s understand what arteries are and why they are important. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. They play a crucial role in maintaining proper circulation and delivering essential nutrients to our organs and tissues. When someone smokes, they expose themselves to toxic chemicals such as nicotine and carbon monoxide, which can lead to various problems with their arteries.
One of the immediate effects of cigarette smoking health effects on arteries is vasoconstriction – a process where blood vessels narrow due to muscle contraction. This results in reduced blood flow and higher blood pressure levels, putting extra strain on the heart. Moreover, these narrowed arteries make it difficult for oxygen and other vital nutrients to reach our tissues effectively.
Furthermore, cigarette smoking also damages the inner lining of our arteries known as endothelium. The presence of toxins in cigarettes causes inflammation and irritation along this delicate lining, leading to atherosclerosis – a buildup of plaque inside arterial walls. This condition not only narrows the artery but can also rupture or form clots that block proper blood flow entirely.
Cigarette smoking health effects also has adverse effects on our cholesterol levels – another major contributor to heart disease. Cigarettes contain high amounts of LDL (bad) cholesterol while reducing HDL (good) cholesterol levels in our body. As a result, excess LDL accumulates on arterial walls causing hardening and narrowing over time.
Sadly, even quitting cigarette smoking health effects does not guarantee complete reversal or repair of these damaged blood vessels. However; studies have shown that within 5 years of quitting cigarettes completely; there is a significant reduction in plaque buildup within coronary arteries compared with active smokers.
A stands for arteries, and it is essential to understand that cigarette smoking health effects, also significantly impairs their ability to function correctly. From vasoconstriction, impaired delivery of nutrients, inflammation, and atherosclerosis to high cholesterol levels – the damage caused by cigarette smoking health effects and extensive and far-reaching. Quitting cigarette smoking can help prevent further harm and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Brain
We all know that cigarette smoking health effects is harmful to our health, but did you know that it also has a significant impact on our brains? The human brain is a complex organ responsible for controlling and coordinating everything we do, think, and feel. So, it’s no surprise that cigarette smoking health effects, can have adverse effects on this vital part of our body.
Nicotine, one of the most addictive substances found in cigarettes, plays a crucial role in how cigarette smoking health affects the brain. When we smoke, nicotine enters our bloodstream and travels to the brain within seconds. Once there, it binds to nicotine receptors on nerve cells and releases neurotransmitters like dopamine, which activate the brain’s reward system. This leads to feelings of pleasure and satisfaction, making smokers crave more nicotine.
However, with repeated exposure to nicotine from smoking cigarettes comes changes in the structure and function of the brain. Studies have shown that long-term use of tobacco can cause thinning of the cortex – the outer layer responsible for decision-making and problem-solving. It also disrupts communication between different regions of the brain that are necessary for cognitive functions such as memory, attention span, and learning. As a result, smokers may experience difficulty concentrating or retaining information.
Moreover, cigarette smoking health effects has been linked to an increased risk of developing certain psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety. Nicotine acts as both a stimulant and a sedative depending on how much is consumed at once – leading to fluctuations in mood levels. Additionally, prolonged nicotine use can cause structural changes in areas responsible for emotional regulation in the brain – leading to heightened emotions or numbing effects.
Aside from these physiological changes brought about by nicotine exposure through cigarette smoke inhalation; other toxic chemicals found in tobacco products also contribute to negative effects on the brain. For instance, carbon monoxide reduces oxygen supply to the brain – causing dizziness or even fainting spells among heavy smokers.
Cigarette smoking health effects, and may have a pleasurable and relaxing effect on the brain initially; but over time, it can cause significant damage to its structure and function. Therefore, quitting cigarette smoking health effects, not only beneficial for your overall health but also vital for maintaining optimal brain function. Remember, it’s never too late to quit – and your brain will thank you.
meanwhile go through these life saving vitamins

Brain Infections:
When we think of cigarette smoking health effects, we often associate it with lung cancer and respiratory illnesses. However, the harmful effects of cigarette smoking health effects extend far beyond the lungs. In fact, research has shown that cigarette smoking health effects and also increase the risk of brain infections.
One of the most common types of brain infection associated with smoking is meningitis. This is a serious condition in which the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord become inflamed. Smoking weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to contracting meningitis from bacteria or viruses. Smokers are also more likely to experience severe symptoms and complications from meningitis compared to non-smokers.
Moreover, smokers are at an increased risk for developing encephalitis – a viral infection that causes inflammation in the brain tissue. This can lead to symptoms such as fever, headache, confusion, and even seizures. Research has shown that smokers have a lower response rate to treatment for encephalitis compared to non-smokers.
In addition to these infections, cigarette smoking health effects, it has also been linked to an increased risk of brain abscesses – pockets of pus that form in the brain due to an infection or injury. These abscesses can cause neurological symptoms like headache, confusion, and weakness in various parts of the body.
Furthermore, heavy smokers are at a higher risk for developing stroke-related infections like cerebral infarction (blockage in blood vessels supplying oxygen to the brain) and intracerebral hemorrhage (bleeding within the brain). The toxins in cigarettes damage blood vessel walls and promote inflammation and blood clots formation – all factors that contribute to these life-threatening conditions.
Cigarette smoke contains thousands of chemicals that can directly damage nerve cells in the brain over time. This can lead to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease later on in life.
It’s important not only for smokers but also those who are exposed to secondhand smoke to be aware of the increased risk of brain infections associated with smoking. Quitting smoking is the best way to prevent these infections and reduce overall health risks. If you or a loved one is struggling with quitting, seek help from a healthcare professional for support and resources. Remember, every part of your body – including your brain – deserves to be treated with care and respect.
Brain Diseases
The brain, being the central command center of our body, is greatly affected by many external factors. One of these factors is smoking, which can lead to various brain diseases. These diseases range from mild cognitive impairments to severe neurological disorders. In this section, we will discuss how smoking affects the brain and its potential consequences.
As soon as a person lights up a cigarette, toxic chemicals start entering their body through inhalation. These chemicals then travel to the brain and disrupt its normal functioning. Nicotine, one of the main components in cigarettes, is highly addictive and can cause changes in the brain’s reward system. It increases dopamine levels, providing smokers a pleasurable sensory experience that encourages them to continue smoking.
One of the most well-known effects of smoking on the brain is its impact on memory and cognitive abilities. Smoking has been linked to an increased risk for developing Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. This is because nicotine can narrow blood vessels in the brain, reducing oxygen flow and causing damage to brain cells responsible for memory and learning.
Moreover, long-term smoking has been associated with decreased gray matter volume in certain areas of the brain related to cognition and emotional regulation. As a result, smokers may have difficulty with decision-making skills and processing emotions effectively.
But it’s not just nicotine that harms our brains; other components present in cigarettes can be equally damaging. For instance, carbon monoxide binds with hemoglobin in our blood when we inhale cigarette smoke instead of oxygen molecules. This reduces the overall supply of oxygen to our brains leading to hypoxia (lack of oxygen). Studies suggest that chronic hypoxia caused by cigarette smoking health effects and can increase one’s risk for cerebral infarction or stroke.
Additionally, heavy smokers are more prone to developing psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety due to disruptions in neurotransmitters caused by tobacco smoke exposure.
Furthermore,long-term smokers are at higher risk for developing Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that affects the movement and coordination. Research has shown that individuals who smoke for more than 15 years are three times more likely to develop Parkinson’s compared to non-smokers.
Cigarette smoking health effects can have detrimental effects on the brain, ranging from memory loss and cognitive impairments to severe neurological disorders. It is crucial to educate ourselves on the potential consequences of our actions and make conscious decisions to protect not just our physical health but also our mental well-being.
Bone Health
Bone health is often overlooked when discussing the harmful effects of smoking, but the truth is that this habit can have a significant impact on our bones. Bones are living organs that provide structure, protect vital organs, and support our body’s movement. In order to maintain healthy bones, it is crucial to understand how smoking affects them.
First and foremost, cigarette smoking health effects and weakens your bones by reducing their density and strength. This is because cigarette smoke contains numerous toxic chemicals such as nicotine, tar, and carbon monoxide which directly interfere with bone growth and development. These substances disrupt the balance between bone formation and removal by inhibiting the activity of osteoblasts (cells responsible for bone formation) while increasing the activity of osteoclasts (cells responsible for bone resorption). As a result, smokers have lower bone mineral density than non-smokers and are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis – a condition in which bones become fragile and prone to fractures.
Moreover, cigarette smoking health effects and interferes with calcium absorption – an essential mineral for building strong bones. Nicotine damages the cells lining the small intestine that are responsible for absorbing calcium from food. This leads to lower levels of calcium in the blood which can weaken your bones over time. Additionally, cigarette smoking health effects and reduces estrogen levels in women – a hormone known to play a critical role in maintaining bone health. Low estrogen levels can lead to accelerated bone loss during menopause, putting women at an increased risk of developing osteoporosis.
Aside from affecting bone density and strength, cigarette smoking health effects and also impairs fracture healing process. After sustaining a broken bone or undergoing surgery to fix it, your body needs precise biochemical signals to initiate healing responses such as forming new blood vessels and collagen production. Cigarette smoking health effects and hinders these processes by constricting blood vessels thus cutting off oxygen supply needed for tissue repair and regeneration.
Chronic cigarette smoking health effects and also is associated with an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis – an autoimmune disorder that causes chronic inflammation and progressive damage to joints. Studies have shown that smoking increases the risk of developing this debilitating disease by up to 50% compared to non-smokers.
Smoking has a detrimental effect on bone health. Its harmful chemicals interfere with the normal functioning of bone cells, reduce calcium absorption, impair fracture healing process, and increase the risk of developing osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Quitting smoking is one of the best ways to protect your bones and maintain overall health.


3 thoughts on “From A to Z: How Smoking Affects Every Part of Your Body”